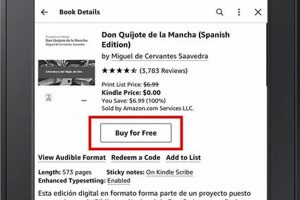
Removing content from a Kindle Paperwhite involves several processes that vary depending on whether the user intends to eliminate the item permanently or simply remove it from the device. One method is to remove a book from the device, freeing up storage space, while another option is to delete it entirely from the Amazon account. The steps required differ depending on the desired outcome.
Properly managing content on a Kindle Paperwhite is essential for optimizing device performance and maintaining a well-organized library. Removing unwanted titles improves the user experience by streamlining navigation and ensuring that only relevant reading material is readily accessible. Furthermore, deleting titles from the Amazon account can be important for managing digital rights and personal preferences.
This discussion will detail the specific procedures for both removing content from the device and permanently deleting it from the associated Amazon account. It will also address potential troubleshooting steps and considerations for managing subscriptions and bundled content.
Tips for Managing Content
Effective management of digital books on a Kindle Paperwhite contributes significantly to device usability and storage efficiency. The following tips outline best practices for removing and organizing content.
Tip 1: Utilize Cloud Storage: Removing a book from the device does not delete it from the Amazon account. The title remains accessible in the cloud and can be downloaded again at any time, provided the device is connected to Wi-Fi.
Tip 2: Differentiate ‘Remove’ and ‘Delete’: The “Remove from Device” option clears space on the Kindle Paperwhite. The “Delete Permanently” option removes the title from the Amazon account, making it irretrievable unless repurchased.
Tip 3: Manage Series and Collections: Organize books into collections for easier navigation. This does not affect storage but improves the browsing experience. To remove a collection, it must first be emptied of all books.
Tip 4: Deregistering the Device: Before selling or gifting a Kindle Paperwhite, deregister it from the Amazon account to prevent unauthorized access to purchased content and personal information. This is found in the device settings.
Tip 5: Consider Subscription Content: If a title was obtained through a Kindle Unlimited or Prime Reading subscription, removing it from the device will not cancel the subscription. To cancel the subscription, manage the account through the Amazon website.
Tip 6: Check for Bundled Content: Some Kindle Paperwhite devices come with pre-loaded content. This content can usually be removed from the device, but may not be removable from the Amazon account depending on the specific offer.
Tip 7: Periodically Review Library: Regularly assess the library to remove unread or unwanted titles. This practice maintains a curated collection and optimizes device storage.
Employing these tips ensures efficient management of content on a Kindle Paperwhite, resulting in an enhanced reading experience and optimal device performance.
The next section will cover common issues encountered while deleting content, and how to resolve them efficiently.
1. Device Storage Management
Device storage management is intrinsically linked to content removal. The fundamental action of eliminating books from a Kindle Paperwhite directly affects the available storage capacity. When a user chooses to remove a book, it is the device’s internal memory that benefits. This is particularly relevant on devices with limited storage, where accumulating numerous large files, such as graphic novels or audiobooks, can quickly deplete available space. Without proactive management, the device’s performance may degrade, and the user experience is negatively impacted. Removing books provides immediate relief from storage constraints, enabling the user to download new content and maintain optimal performance.
The act of removing books differs distinctly from permanent deletion. Removing a book merely clears it from the device, while the book remains accessible in the Amazon cloud library associated with the account. A real-life example is a user who has completed reading a lengthy novel. Rather than keeping the large file occupying valuable storage space, the book can be removed. Should the user wish to reread the book in the future, it is readily available for redownload from the cloud. This highlights the practical significance of understanding the nuances of content removal versus permanent deletion. Furthermore, managing device storage effectively extends the lifespan of the Kindle Paperwhite by reducing unnecessary strain on the system’s resources.
In summary, device storage management, facilitated by the ability to remove content, is critical for maintaining the operational efficiency of a Kindle Paperwhite. It allows users to curate their on-device library based on current reading interests, freeing up space for new content and ensuring smooth device performance. The challenge lies in consistently managing the digital library to avoid storage bottlenecks and maximize the device’s functionality. This active management strategy is a cornerstone of optimal Kindle Paperwhite utilization.
2. Amazon Account Deletion

Amazon account deletion represents the most comprehensive form of content removal, distinct from merely removing a book from a Kindle Paperwhite device. Deleting a title from the Amazon account eliminates it from the user’s entire digital library, rendering it inaccessible across all devices registered to that account. This action is irreversible unless the title is repurchased. The connection to device management is indirect but critical: while removing a title from the Paperwhite frees up space, account deletion permanently revokes ownership. The importance lies in understanding the implications of such a drastic action.
A scenario illustrating the practical significance of this distinction involves a user who inadvertently deletes a frequently referenced textbook from their Amazon account. After realizing the mistake, the user must repurchase the book to regain access. This exemplifies the cause and effect relationship between account deletion and content availability. Moreover, the digital rights management associated with Kindle books dictates that ownership resides within the Amazon ecosystem. Deleting the account essentially forfeits these rights. One could also encounter a situation where a user wishes to transfer a Kindle book to a different account. However, deleting it and expecting to easily “transfer” by gifting the title doesn’t work, as gifting requires another purchase.
In summary, while removing books from a Kindle Paperwhite offers a localized solution for managing device storage, deleting titles from the Amazon account involves a permanent revocation of content ownership. The challenge is in discerning the appropriate action based on the user’s long-term needs and intentions. Understanding the ramifications of account deletion is paramount to avoid unintentional loss of purchased content and ensure informed management of one’s digital library. This comprehensive action offers complete removal, but requires careful consideration.
3. Content Synchronization Implications
Content synchronization plays a critical role in the management of digital books across multiple devices linked to an Amazon account. Understanding the implications of synchronization is essential when removing content from a Kindle Paperwhite, as the actions taken can have varying effects on other registered devices.
- Automatic Download Settings
When automatic download settings are enabled on a Kindle Paperwhite, any book purchased or added to the Amazon account is automatically downloaded to the device. Removing a book from the Paperwhite will not delete it from the account, and it may be automatically downloaded again if this setting remains active. This behavior is important to note, as simply removing a title may not prevent its reappearance on the device.
- Cloud Storage and Availability
All purchased Kindle books are stored in the Amazon cloud. Removing a book from the Kindle Paperwhite only deletes the local copy; the book remains available for download from the cloud. This means that even after removal, the book appears in the library but must be re-downloaded to be read. A user with multiple Kindles or the Kindle app on other devices will find the book still available in their cloud library, highlighting the persistence of content in the Amazon ecosystem.
- Synchronization of Reading Progress
The Whispersync feature synchronizes reading progress, bookmarks, and notes across devices. If a user removes a book from one device, reading progress is generally retained in the cloud. If the book is re-downloaded, the user can resume reading from where they left off. This interconnectivity means removing content does not necessarily erase personal annotations or reading history associated with the book.
- Managing Multiple Devices
Users with multiple Kindle devices need to consider the implications of synchronization when removing content. Removing a book from one device only affects that specific device. To remove the book entirely, it must be either removed from each individual device or deleted from the Amazon account altogether. This decentralized control requires a mindful approach to maintaining a consistent library across devices.
In conclusion, understanding content synchronization is essential for effective management of a digital library across multiple devices. While removing content from a Kindle Paperwhite frees up local storage, the cloud-based nature of Kindle books and the synchronization features mean that content is still accessible from other devices. To truly delete a book, it must be removed from the Amazon account, or each registered device. These factors highlight the nuanced relationship between “Content Synchronization Implications” and the process of removing content from a Kindle Paperwhite.
4. Subscription Service Interaction
Subscription services, such as Kindle Unlimited and Prime Reading, introduce a specific layer of complexity to managing content on a Kindle Paperwhite. These services grant access to a rotating catalog of books, which users can borrow and read as part of their subscription. Removing a borrowed book from a Kindle Paperwhite acquired through a subscription differs significantly from removing a purchased title. While a purchased book can be removed from the device or permanently deleted from the Amazon account, a borrowed book can only be removed from the device. Its access is inherently tied to the active subscription. The cause-and-effect relationship here is direct: maintaining an active subscription provides continued access to previously borrowed titles, even after they have been removed from the device. Canceling the subscription, conversely, revokes access to all borrowed books, regardless of their presence on the device.
Consider a user who borrows ten books via Kindle Unlimited. Removing these books from their Kindle Paperwhite does not terminate their access, as long as the subscription remains active. The books can be re-downloaded at any time. However, if the user cancels their Kindle Unlimited subscription, these ten books will no longer be accessible, even if they were previously downloaded onto the device. This illustrates the practical significance of understanding that subscription content is governed by the terms of the subscription itself, rather than the standard purchase-and-ownership model. Furthermore, these types of subscription-based service interactions often limit the user in terms of sharing, or “gifting” the books to other users, highlighting the restrictions in digital-ownership of the materials.
In summary, Subscription Service Interaction significantly influences content management on a Kindle Paperwhite. Removing borrowed books only clears device storage, while the subscription’s status determines continued access. The challenge lies in differentiating between purchased and borrowed content and managing subscriptions proactively to align with reading habits and needs. Understanding this interaction ensures users are not caught off guard by unexpected access restrictions or continued availability of unwanted titles. The interplay between subscription services and content removal is a crucial aspect of managing a Kindle Paperwhite effectively.
5. Troubleshooting Removal Issues
Effective operation of a Kindle Paperwhite requires the ability to remove content as needed. Instances may arise where the removal process encounters difficulties, necessitating troubleshooting. These issues can range from minor software glitches to more complex problems related to content synchronization or account authorization. Understanding common removal issues and their resolutions is essential for maintaining a functional and organized Kindle library.
- Frozen Interface
A frozen interface can impede the removal process by preventing access to the necessary menu options. This typically manifests as an unresponsive screen when attempting to select “Remove from Device” or “Delete Permanently.” The most common cause is a temporary software glitch. A solution involves performing a hard reset of the Kindle Paperwhite by holding the power button for an extended period (typically 40 seconds) until the device restarts. This clears the device’s memory and often resolves the unresponsiveness. Failing a hard reset, connecting the device to a power source and attempting the reset again may be necessary. Unresolved freezing issues could point to potential hardware malfunctions.
- Content Synchronization Conflicts
Synchronization conflicts can occur when the Kindle Paperwhite struggles to communicate with Amazon’s servers. This can prevent the device from accurately reflecting the user’s actions, such as removing a book. In such cases, the book may appear to be removed but reappears after a synchronization cycle. Resolving this involves ensuring a stable Wi-Fi connection and manually initiating a synchronization by navigating to the settings menu and selecting “Sync My Kindle.” If the issue persists, deregistering and reregistering the device can force a complete refresh of the content library.
- Authorization Problems
Authorization problems can arise if the Kindle Paperwhite is not properly registered to the Amazon account. This prevents the device from verifying content ownership, which can interfere with content removal. Signs of authorization issues include error messages related to DRM (Digital Rights Management) or inability to access purchased content. The resolution involves verifying the registration status within the device settings. If necessary, deregistering the device and then reregistering it with the correct Amazon account credentials will reestablish authorization and enable content removal.
- Storage Management Errors
Storage management errors can occur when the Kindle Paperwhite’s storage is nearly full. This can disrupt various device functions, including content removal. When the device is unable to allocate sufficient resources for the removal process, error messages may appear, or the removal may fail silently. The solution involves removing other unnecessary content, such as downloaded periodicals or large files, to free up storage space. After creating sufficient space, attempting the removal process again should resolve the issue.
Addressing these common troubleshooting points helps ensure effective content removal from a Kindle Paperwhite. While these solutions typically resolve most issues, persistent problems may indicate more severe technical malfunctions requiring professional assessment. Proper management and proactive maintenance contribute to an uninterrupted reading experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the removal of digital books from a Kindle Paperwhite device. The following questions and answers aim to provide clarity on the nuances of content management within the Kindle ecosystem.
Question 1: Is removing a book from a Kindle Paperwhite the same as deleting it?
No, removing a book from the device only frees up storage space. The title remains accessible in the Amazon cloud library associated with the account and can be re-downloaded at any time, provided a Wi-Fi connection is available. Deleting the book, conversely, permanently removes it from the account.
Question 2: What happens to my notes and highlights if I remove a book from my Kindle Paperwhite?
Notes and highlights associated with a book are typically stored in the Amazon cloud via Whispersync. If the book is re-downloaded to the same or a different Kindle device registered to the same account, the notes and highlights will generally be synchronized and restored. However, deleting the book permanently from the Amazon account may result in the loss of this data.
Question 3: How do I permanently delete a book from my Amazon account using my Kindle Paperwhite?
Permanent deletion cannot be performed directly from the Kindle Paperwhite device. The process requires logging into the Amazon account via a web browser, navigating to the “Manage Your Content and Devices” section, locating the title, and selecting the “Delete” option. This action is irreversible unless the book is repurchased.
Question 4: If I have multiple Kindle devices, will removing a book from one device remove it from all of them?
Removing a book from one Kindle device does not automatically remove it from other devices registered to the same account. The book must be individually removed from each device or deleted from the Amazon account to achieve complete removal.
Question 5: What happens to borrowed books from Kindle Unlimited or Prime Reading if I remove them from my Kindle Paperwhite?
Removing a borrowed book from the device only clears storage space. As long as the Kindle Unlimited or Prime Reading subscription remains active, the book can be re-downloaded. Cancelling the subscription revokes access to all borrowed titles, regardless of whether they are currently downloaded on the device.
Question 6: Why can’t I remove some books from my Kindle Paperwhite?
Inability to remove books may be due to synchronization issues, authorization problems, or storage management errors. Ensure a stable Wi-Fi connection, verify the device is registered to the correct Amazon account, and free up storage space by removing other content. A hard reset of the device may also resolve temporary software glitches preventing removal.
Understanding these points ensures informed management of digital content and mitigates potential issues encountered while operating a Kindle Paperwhite. The distinction between removing and deleting is paramount to avoid unintended loss of purchased content.
The following section will cover alternative devices that can be used as replacement for Kindle Paperwhite.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of deleting books from Kindle Paperwhite has elucidated the critical distinctions between removing content from the device and permanently deleting it from the associated Amazon account. The functionalities and implications of each action were detailed, alongside providing practical advice for managing a digital library, troubleshooting removal issues, and understanding how subscriptions can impact accessibility. These concepts are pivotal for maintaining an organized and efficiently operating Kindle Paperwhite.
Effective management of digital content demands a deliberate approach to device maintenance and an awareness of account settings. It is incumbent upon the user to consider the long-term effects of content deletion and to proactively manage the digital library in accordance with individual needs and preferences. Continued vigilance in this practice will ensure optimal utilization of the Kindle Paperwhite and safeguard against unintended content loss.